Zappar Camera
Before setting up Augmented Reality tracking, you must first add (or replace any existing camera you have in your .zcomp with) a ZapparCamera component to your Hierarchy.
To add a ZapparCamera component to an existing project, you will first need to install the Augmented Reality by Zappar package from the dependencies browser if you have not already.
- Click on the + (plus) icon in your Hierarchy (or right click on a Group Node)
- Find the
ARcomponent category and from here, selectZapparCamera
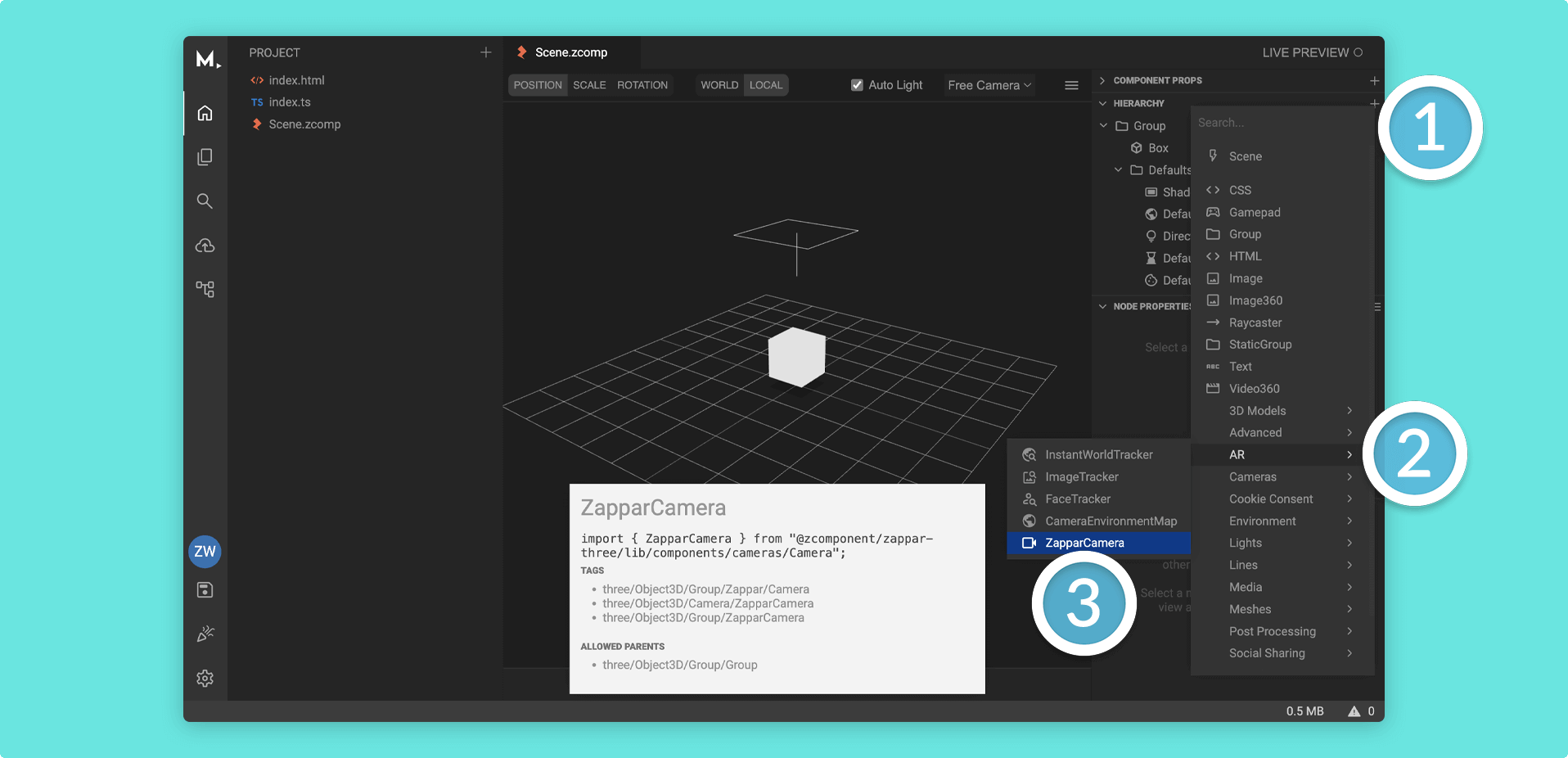
The ZapparCamera will give you the correct parameters to track content, as well as request the appropriate permissions to access the camera and motion sensors on the user’s device.
ZapparCamera properties
Section titled “ZapparCamera properties”The ZapparCamera component has the following specific properties:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
Pose Mode | Describes how the camera moves around in the three.js scene. See more below. |
Origin Anchor | The camera will move and rotate in world space around the anchor at the specified origin (component in the Hierarchy). |
Rear Mirror Mode | Describes whether your camera (Poses) or entire canvas (CSS) is mirrored or not (None) when using the rear facing camera. |
User Mirror Mode | Describes whether your camera (Poses) or entire canvas (CSS) is mirrored or not (None) when using the user facing camera. |
Camera Direction | Choose whether the camera is rear or user facing. |
Far | Alter the far clipping plane. |
Near | Alter the near clipping plane. |
Pose Mode
Section titled “Pose Mode”Mattercraft provides multiple modes for the camera to move around in the three.js scene.
| Pose Mode | Description |
|---|---|
Default | The camera will stay at the origin of the scene, pointing down the negative Z axis. Any tracked anchors will move around in your scene as the user moves the physical camera and real-world tracked objects. |
Attitude | The camera will stay at the origin of the scene, but rotates as the user rotates the physical device. When the experience initializes, the negative Z axis of world space points forward in front of the user. |
AnchorOrigin | The origin of the scene is the center of the anchor specified by the camera’s Origin Anchor parameter. In this case, the camera moves and rotates in world space around the anchor at the origin. |
The correct choice of camera pose will depend on your given use case and content. Here are some examples you might like to consider when choosing which is best for you:
- To have a light that always shines down from above the user, regardless of the angle of the device or anchors, use the
Attitudepose mode and place a light shining down the negative Y axis is world space. - In an application with a physics simulation of stacked blocks, and with gravity pointing down the negative Y axis of world space, using the
AnchorOriginpose mode would allow the blocks to rest on a tracked image regardless of how the image is held by the user. - In a similar application, the
Attitudepose mode would allow the user to tip the blocks off the image by tilting it.
Tracking content
Section titled “Tracking content”With a ZapparCamera inside your .zcomp, you can then start using the following Augmented Reality tracking types: